Large files
实验目的:
- 扩充 inode 的
addrs数组,为其减少一个直接块,增加一个二级间接块,其存储一级间接块的地址 - 修改
bmap(),使得其能定位二级间接块里的数据块 - 修改
itrunc(),使其能释放二级间接块及其中的所有块
addrs 数组的结构:
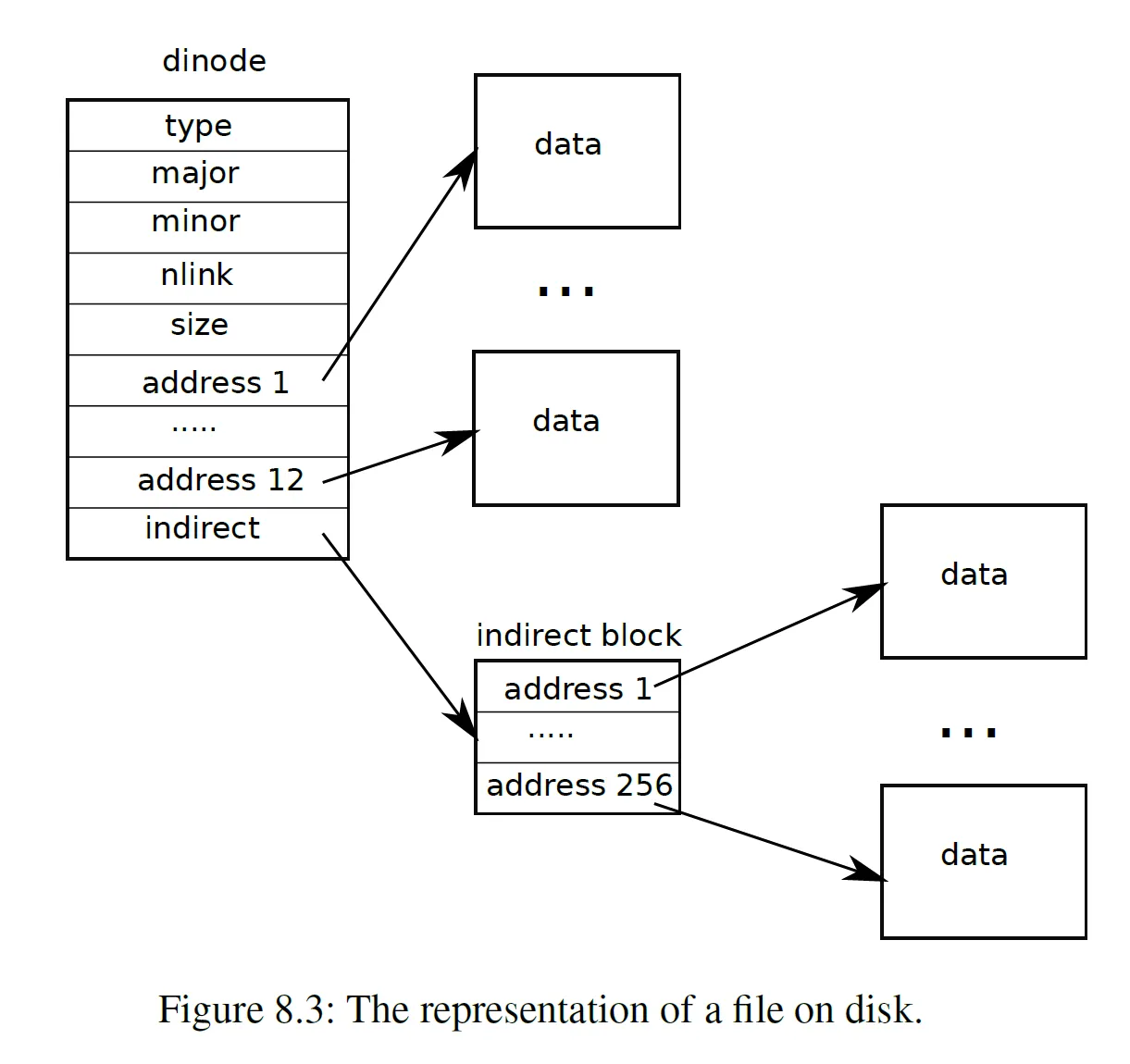
首先修改全局变量以及 struct inode/dinode:
#define NDIRECT 11
#define NINDIRECT (BSIZE / sizeof(uint))
#define MAXFILE (NDIRECT + NINDIRECT + NINDIRECT * NINDIRECT)
// On-disk inode structure
struct dinode {
short type; // File type
short major; // Major device number (T_DEVICE only)
short minor; // Minor device number (T_DEVICE only)
short nlink; // Number of links to inode in file system
uint size; // Size of file (bytes)
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2]; // Data block addresses
};
// in-memory copy of an inode
struct inode {
uint dev; // Device number
uint inum; // Inode number
int ref; // Reference count
struct sleeplock lock; // protects everything below here
int valid; // inode has been read from disk?
short type; // file or directory
short major;
short minor;
short nlink;
uint size;
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2];
};接着为 bmap() 增加索引二级间接块的逻辑:
static uint
bmap(struct inode *ip, uint bn)
{
uint addr, *a;
struct buf *bp;
if(bn < NDIRECT){
if((addr = ip->addrs[bn]) == 0)
ip->addrs[bn] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
return addr;
}
bn -= NDIRECT;
if(bn < NINDIRECT){
// Load indirect block, allocating if necessary.
if((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT]) == 0)
ip->addrs[NDIRECT] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if((addr = a[bn]) == 0){
a[bn] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
return addr;
}
bn -= NINDIRECT;
if (bn < NINDIRECT * NINDIRECT) {
int id = bn / NINDIRECT;
int off = bn % NINDIRECT;
if ((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]) == 0) // 先检查二级间接块是否存在
ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint *)bp->data;
if ((addr = a[id]) == 0) { // 检查其中的一级间接块是否存在
a[id] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp); // 记录修改
}
brelse(bp); // 释放二级间接块
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr); // 读取一级间接块
a = (uint *)bp->data;
if ((addr = a[off]) == 0) {
a[off] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
return addr;
}
panic("bmap: out of range");
}修改 itrunc() 的逻辑,使其能够释放二级间接块:
void
itrunc(struct inode *ip)
{
int i, j;
struct buf *bp;
uint *a;
for(i = 0; i < NDIRECT; i++){
if(ip->addrs[i]){
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[i]);
ip->addrs[i] = 0;
}
}
if(ip->addrs[NDIRECT]){
bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT]);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
for(j = 0; j < NINDIRECT; j++){
if(a[j])
bfree(ip->dev, a[j]);
}
brelse(bp);
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT]);
ip->addrs[NDIRECT] = 0;
}
// 释放二级间接块
if (ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]) {
bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]);
a = (uint *)bp->data;
struct buf *bps;
uint *b;
for (j = 0; j < NDIRECT; ++j) {
if (a[j]) { // 一级间接块存在,则需要先释放其中的数据块
bps = bread(ip->dev, a[j]);
b = (uint *)bps->data;
for (int i = 0; i < NDIRECT; ++i) {
if (b[i])
bfree(ip->dev, b[i]);
}
brelse(bps);
bfree(ip->dev, a[j]); // 释放一级间接块
}
}
brelse(bp);
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]);
ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1] = 0;
}
ip->size = 0;
iupdate(ip);
}Symbolic links
硬链接是同一个文件的多个目录入口,指向相同的 inode;而软链接则是一个独立的文件,存储的是目标文件的路径。
实验目的:
- 添加并实现
symlink(char *target, char *path)系统调用,使得为target创建path软链接 - 修改
open(),添加对软链接的处理
对于 symlink() 系统调用的添加不再赘述。
在 fcntl. h 中添加 O_NOFOLLOW,由于不能与已有标志重叠,所以设置为 0x800
#define O_RDONLY 0x000
#define O_WRONLY 0x001
#define O_RDWR 0x002
#define O_CREATE 0x200
#define O_TRUNC 0x400
#define O_NOFOLLOW 0x800symlink() 的实现:创建一个 inode,设置类型为 T_SYMLINK,然后向 inode 中写入 path 即可
uint64
sys_symlink(void)
{
char target[MAXPATH];
memset(target, 0, sizeof(target));
char path[MAXPATH];
if(argstr(0, target, MAXPATH) < 0 || argstr(1, path, MAXPATH) < 0){
return -1;
}
struct inode *ip;
begin_op();
if((ip = create(path, T_SYMLINK, 0, 0)) == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
if(writei(ip, 0, (uint64)target, 0, MAXPATH) != MAXPATH){
// panic("symlink write failed");
return -1;
}
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return 0;
}在 sys_open 中添加对符号链接的处理:
uint64
sys_open(void)
{
...
if(ip->type == T_DEVICE && (ip->major < 0 || ip->major >= NDEV)){
...
}
if(ip->type == T_SYMLINK){
if(!(omode & O_NOFOLLOW)){ // 检查是否要求不解析链接
int cycle = 0;
char target[MAXPATH];
while(ip->type == T_SYMLINK){
if(cycle == 10){ // 最大递归深度10
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1; // max cycle
}
cycle++;
// 读取目标路径
memset(target, 0, sizeof(target));
readi(ip, 0, (uint64)target, 0, MAXPATH);
iunlockput(ip);
// 根据目标路径获取新的inode
if((ip = namei(target)) == 0){
end_op();
return -1; // target not exist
}
ilock(ip);
}
}
}
if((f = filealloc()) == 0 || (fd = fdalloc(f)) < 0){
...
}
...
}- 文件路径指向一个软链接时,系统需要递归地解析链接目标,直到找到最终的非链接文件或达到最大递归深度